Distribution Transformer
Types, Diagram, Parts, Working principle.
1- What is the Distribution Transformer?:

The transformer is a boon of electrical system which is used for voltage transformation in transmission and distribution line. it is used for high voltage to low voltage and low voltage to high voltave. It has two type main function which is mentioned below.
- Low to High voltage transformation:Low to high voltage(11 KV to 400KV) is used in transmission lines for voltage transmission.
- High to low voltage transormationHigh to low voltage(11KV or 33KV to 415V) is ued in distribution line for utilizatio of consumer.
for us it is also used in a bulk above 500 KVA. It is used as an outdoor or open area and oil is used in this. The transformer oil is also called as insulation oil. The efficiency of it is very good in comparison to others.
The function of oil is two types, one is arc quenching in tank and reduces the winding temp It is used as a cooling medium for winding and core during load and its dielectric strength is very good.
Different type categories of transformer are available as per requirements of industries or consumer. Everyone can see easily anywhere so we are going to discuss about oil type transformer. it is low cost against dry type transformer
2- Connection / Circuit diagram of distribution transformer.:
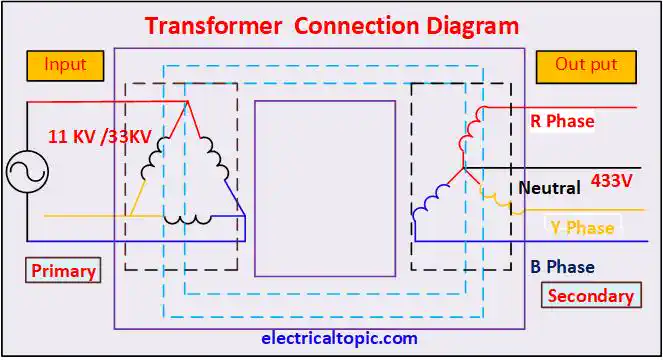
3- Working principle of Distribution Transformer.
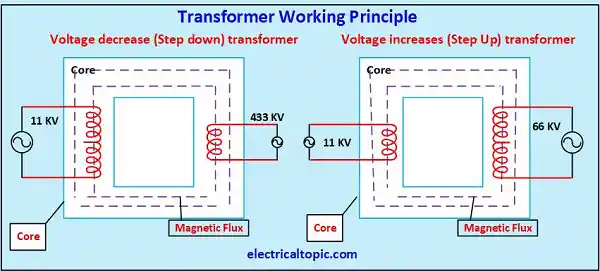
Transformer is an electrical static device. The main function of transformer is voltage transformation as voltage increasing and decreasing on same frequency. Voltage is increased for power transmission line and voltage is decreased for power distribution line.
1- Voltage Decrease Working Principle (Step down)
- If we want to decrease alternative current (AC) voltage in output as the transformer has two windings where one is primary winding and 2nd is secondary winding.
- 11kv to 433 voltage, 33 KV to 440 voltage, 66 KV to 33 KVetc. than primary winding turns should be more and less turn should be secondary winding.
- When high AC voltage is applied into primary winding which is installed on insulated iron core than magnetic flux generated on insulated iron core and it will transfer into secondary by mutual inductance faraday law. Due to less turns the output voltage will be received as low.
- For example, if 11 KV HT voltage is applied on primary winding then the 433-output voltage is received at secondary winding. if we talk about current and voltage relation. High voltage, low current changed into low voltage high current.
2- Voltage increase Working Principle (Step Up)
- If we want to increase AC voltage in output as 11KV to 33 KV voltage, 33 KV to 66 KV voltage, 66 KV to 132 KV etc. than primary winding turns should be less and more turn should be secondary winding.
- When low AC voltage is applied into primary winding which is installed on insulated iron core than magnetic flux generated on insulated iron core and it will transfer into secondary winding because it is also installed on same insulated iron core by mutual inductance faraday law. Due to more turns the output voltage will be received as more.
- For example, if we applied 11 KV voltage on primary winding than we will get 33KV volts on secondary winding. if we talk about current and voltage relation then Low voltage, high current changed into high voltage, low current.
4 - Parts of Oil Type Transformer:
- Tank
- Iron core
- Winding
- terminal and bushing
- Expansion vent
- On load tap changer
- Oil and Winding Temp Indicator
- Buchholz relay
- Conservator
- Silica gel breather
- Transformer oil
4 - What is the Transformer oil and why it is used?
Transformer oil is known as insulated oil. It is used for heat removing from core and windings at high temp and any arching in tank. Between conductor it works as insulator. it has excellent dielectric strengthen. It has high flash point and thermal stability. It comes in market as two types.
- Paraffinic oil:
- Naphthenic oil:oil is used in mostly because it has good dielectric strength in high temperature stability. The boiling point of this oil is 425°c.
Importance of Transformer Oil:
- For cooling:
- For insulation
- Corona effect: