Digital Ampere (Ammeter) Meter
Diagram, Working Principle and Types.
1 - Ampere(ammeter) Meter:

Ampere meter is a electrical instrument measuring device which is used for current measuring in circuit It is connected to the series in phase wire. Two types ampere meters are used like as analogs meter and digital meters.Both types meter are used as single phase and three phase.
2 - Ampere Meter Wiring Diagram:
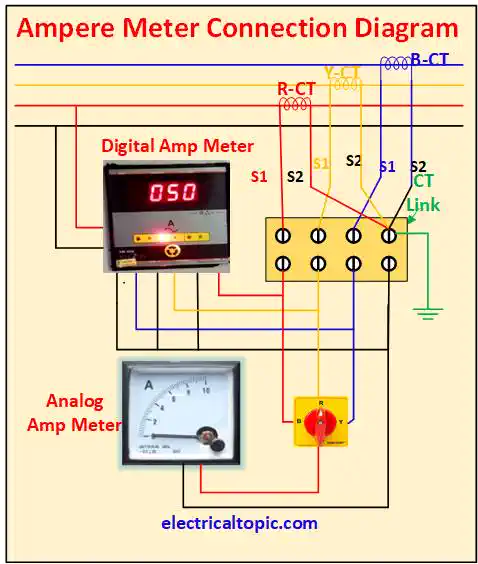
3 - Types of Ampere Meter:
1- Analog Ampere Meter:
Analog ampere meter is used as electromagnetic function. A pointer needle is moved on measuring dial according current value . The value may be 0 to 5 or as per requirement. Accuracy is not good in comparison of digital meter.
2- Digital Ampere Meter
Digital ampere meter is using in industries a lot. A single device can easily measure the single phase and
three phases current. Current transformer is used for receiving current value without connecting in series.
A rounded or square CT is fixed on phase wire where phase wire works as primary and CT coil works as
secondary coil. CT secondary wire is connected to the digital meter for receiving amp value on display.
4 - Working Principle of Ampere Meter.:
Analog and digital amp meters are used for measuring current. The details are given below mentioned.
Analog Meters
Analog meter works on electromagnetic function. A magnetic coil is used and connected with series in analog meter. When circulate the load current in magnetic coil then magnetic flux is produced and needle of pointer which shows the value of current on display.
Digital Ampere Meter
Now a days or laterally the digital meters are mostly used because its accuracy is good as per analog.
Current transformer are used for digital amp meter. CTs are fixed in phase wire where phase wire works as
primary and secondary wire is connected to the digital amp meter.
A current signal is received in
digital amp meter and the value of current is showed on display by microprocessors. One CT is used for
single phase and three CTs is used for three phases.
5 - What is Ampere Meter used for:
Ampere meter is used where the load calculation is must. we can get circuit load of equipment and it could be calculated load in watt, kilowatt and kwh. Now a days it is using in domestic, industries,electrical generation, transmission and distribution.